Palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions have become a versatile tool in organic synthesis for the construction of carbon-carbon as well as carbon-heteroatom bonds.
2 Notably, they have evolved into a synthetically attractive transformation in targeting pharmaceutically useful intermediates.
3 Our research group has been engaged in developing several series of indolylphosphine ligands for numerous cross-coupling reactions.
4 In 2008, we reported the application of
CM-phos, which showed excellent catalytic activities towards the first palladium-catalyzed amination (C-N bond formation) and Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reaction (C-C bond formation) of aryl mesylates.
5 The dimeric Pd-
CM-phos complex also showed the same reactivity as in the
in situ generated catalyst (Figure 1). Later,
CM-phos has proven to be an excellent ligand
6 for various Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions with aryl mesylates and tosylates (e.g., Hiyama coupling,
7 Sonogashira coupling,
8 reduction,
9 titanium coupling,
10 and C-H arylation).
11
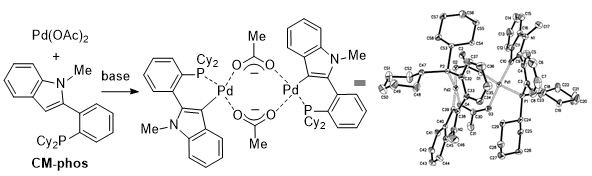
Figure 1. X-ray crystal structure of dimeric Pd/CM-phos complex
Further Investigations in Suzuki-Miyaura Cross-coupling of Aryl Mesylates/Tosylates
The use of
CM-phos as a supporting ligand allowed the expansion of the scope of Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reactions. In 2008, an extension of the Suzuki-Miyaura coupling of (hetero)aryl tosylates was disclosed with 0.2 mol% Pd, and the capability of deactivated tosylates as the coupling electrophiles was showcased (Scheme 1).
12 Sterically hindered arylboronic acids, potassium aryltrifluoroborates and aryl pinacol boronates were suitable coupling nucleophiles, affording excellent product yields. Notably, the coupling of heteroaryl tosylates proceeded smoothly without deleterious effects on the product yield, even at room temperature.
Scheme 1. Pd-Catalyzed Suzuki-Miyaura Cross-Coupling of (Hetero)aryl and Alkenyl Tosylates
In 2010, the Suzuki-Miyaura coupling of (hetero)aryl mesylates with potassium aryltrifluoroborates was further examined (Scheme 2) using the Pd/
CM-phos catalyst system. Moderate-to-excellent product yields were achieved with a palladium loading of 1.0-2.5 mol%.
13 Remarkably, potassium heteroaryltrifluoroborates were feasible partners in the coupling reactions. Specifically, the coupling of thienyl trifluoroborate salt resulted in higher yields compared to the corresponding thienylboronic acid, even with a lower catalyst loading and a shorter reaction time. Furthermore, potassium vinyl- and alkyltrifluoroborate salts were also evaluated under this catalyst system and good product yields were obtained.
Scheme 2. Pd-Catalyzed Suzuki-Miyaura Cross-Coupling of (Hetero)aryl Mesylate and Potassium (Hetero)aryl/vinyl/alkyltrifluoroborates
Subsequently, the Pd/
CM-phos catalyst system was successfully employed in the general Suzuki-Miyaura coupling of alkenyl mesylates and tosylates (Scheme 3).
14 The reactions proceeded under mild conditions (50 ℃), giving good-to-excellent product yields. Notably, hindered tri-
ortho-substituted coupling products were efficiently afforded from bulky alkenyl tosylates and arylboronic acids. Additionally, alkenyl mesylates containing a chloro substituent served as an effective coupling partner, and the chloro-group remained intact which is beneficial for further transformations.
Scheme 3. Pd-Catalyzed Suzuki-Miyaura Cross-Coupling of Alkenyl Mesylates/Tosylates
In 2019, the Pd/
CM-phos catalyst system was extended to synthesize a diverse array of functionalized flavones, using tosyloxy- and mesyloxyflavones as substrates (Scheme 4A)
15 The reaction proceeded smoothly with palladium loading as low as 0.1 mol%. It was remarkable that the hydroxy group in tosyloxyflavone remained intact post-coupling. Furthermore, the catalyst system exhibited exceptional site selectivity towards ditosylated chrysin, facilitating the formation of the desired diarylated flavone with two distinct aryl groups (Scheme 4B).
Scheme 4. Pd-Catalyzed Suzuki-Miyaura Cross-Coupling of Mesyloxy/Tosyloxyflavones and Its Applications in Site Selective Coupling
Utilizing the Pd/
CM-phos system, the synthesis of a flavone-scaffold-containing inhibitor of DNA-dependent protein kinase was accomplished with an overall 30% yield,
15 surpassing the productivity of the original synthetic approach in terms of yield (Scheme 5).
16Scheme 5. Synthesis of a DNA-dependent Protein Kinase by Pd-Catalyzed Suzuki-Miyaura Cross-Coupling of Tosyloxyflavones
In 2016, Zhang and co-workers applied the Pd
2(dba)
3/
CM-phos catalyst system for the Suzuki-Miyaura coupling of
gem-difluoroalkenyl tosyaltes with phenylboronic acid, affording the trisubstituted alkene with excellent yields (Scheme 6).
17Scheme 6. Synthesis of gem-difluroroalkenylated arene through Suzuki-Miyaura Coupling
In 2020, a series of bridged (π-extended) stilbenes was investigated by Suzuki and Konishi, and it was discovered that BPST[7] and DPB[7] express superb aggregation-induced emission properties. In the synthesis of the bridged stilbenes, Pd(OAc)
2/
CM-phos served as the catalyst system in a critical step of coupling alkenyl tosylates with arylboronic acids (Scheme 7).
18Scheme 7. Synthesis of Bridged Stilbenes
Further Investigations in Buchwald-Hartwig Amination of Aryl Mesylates/Tosylates
The use of Pd/
CM-phos catalyst system further allowed the expansion of the scope of Buchwald-Hartwig amination reactions. After the first report of amination of aryl mesylates, an extension of the Buchwald-Hartwig amination of aryl/alkenyl tosylates was demonstrated with a diverse array of amines including arylamines, aliphatic amines, and NH-heterocycles (Scheme 8).
19 In particular, α-chiral amines were also applicable, with enantioselectivity of the product being maintained despite the potential β-elimination of the Pd-N-CHR
2 intermediate. This prevents the subsequent reinsertion of the flipped C(sp
2)-imine moiety, which would otherwise ruin the enantiomeric purity of the product.
20 Remarkably, the amination proceeded smoothly in aqueous medium and solvent-free conditions without deleterious effect.
Scheme 8. Pd-Catalyzed Amination of Aryl Tosylates
In 2019, the Pd-catalyzed amination of tosyloxyflavones was demonstrated using Pd/
CM-phos catalyst system (Scheme 9).
15 Arylamines and cyclic and acyclic aliphatic amines were coupled with the tosyloxyflavones to give the
N-arylated products in good-to-excellent yields.
Scheme 9. Pd-Catalyzed Amination of Tosyloxyflavones
Cyanation is a crucial catalytic reaction, as the resulting nitrile group can be converted into a variety of functional groups.
21 The Pd/
CM-phos catalyst system was employed in the first Pd-catalyzed cyanation of aryl mesylates mediated by K
4[Fe(CN)
6]•3H
2O (Scheme 10A).
22 Interestingly, the use of water as a solvent or co-solvent is critical for the success of cyanation. A one-pot cascade synthesis of an
N-aryl aminobenzonitrile was achieved through the cyanation of aryl tosylate followed by the
N-arylation of the amino group (Scheme 10B). This synthetic pathway is particularly attractive for further functionalization, as it eliminates the need to isolate the initial nitrile-substituted intermediates.
Scheme 10. Pd-Catalyzed Cyanation and Sequential One-Pot Two-Step Cyanation/Amination
Polyfluoroarenes are commonly found in biologically active compounds, pharmaceutically useful molecules,
23 natural products, and functional materials.
24 Palladium-catalyzed C-H arylation of polyfluoroarenes with aryl tosylates and mesylates using Pd/
CM-phos catalyst system was disclosed by Kwong and co-workers in 2012 (Scheme 11A).
25 Additionally, related cathepsin TbcatB inhibitors, consisting of -C
6F
5, N-Ar, and -CN moieties,
26 were synthesized through tandem one-pot sequential C-H arylation/
N-arylation reactions (Scheme 11B).
Scheme 11. Pd-Catalyzed C-H Arylation of Polyfluoroarene and Sequential One-Pot Two-Step C-H Arylation/Buchwald-Hartwig Amination
The first C-P bond formation of aryl mesylates/tosylates with dialkyl phosphite was reported using the Pd/
CM-phos catalyst system (Scheme 12A).
27 It is worthy to note that the aryl tosylates with unprotected amino group was compatible under a Pd loading of 1.5 mol%, achieving an 80% yield. This compatibility is advantageous for further transformations, as demonstrated by a one-pot sequential reaction of C-P and C-N bond formation (Scheme 12B), giving 3-(hetero-arylamino)phenylphosphonate - a key functionality in potential CDK9/CycT1 inhibitors.
28Scheme 12. Pd-Catalyzed Phosphorylation of Aryl Tosylates/Mesylates and Sequential One-Pot Two-Step Phosphorylation/Buchwald-Hartwig Amination
New Pd/CM-phos-type Ligands Catalyst Systems for Suzuki-Miyaura Cross-coupling of Aryl Mesylates/Tosylates
In 2011, a more electron-rich phosphine ligand with
CM-phos scaffold was designed by introducing a methoxy group at the
para-position to the -PCy
2 moiety (i.e.,
MeO-CM-phos, Scheme 13A) to facilitate the oxidative addition process in the cross-coupling reaction.
29 The Pd/
MeO-CM-phos was first employed in the borylation of aryl mesylates and tosylates to afford a wide range of aryl pinacol boronate products. Subsequently, one-pot two-step experiments were carried out in the sequence of borylation-Suzuki coupling to give the unsymmetrical biaryl products (Scheme 13B).
Scheme 13. Pd-Catalyzed Borylation of Aryl Tosylates/Mesylates and One-Pot Two-Step of Borylation/Suzuki Coupling
New Pd/CM-phos-type Ligands Catalyst Systems for Buchwald-Hartwig Amination of Aryl Mesylates/Tosylates
In 2018, the electron-rich
MeO-CM-phos was further utilized in Pd-catalyzed
N-arylation of sulfoximines with aryl tosylates/mesylates (Scheme 14).
30 Using the original Pd/
CM-phos catalyst system, the desired
N-arylated sulfoximine was obtained in 89% yield. By introducing an electron-donating methoxy group at the
para-position to the -PCy
2 moiety in
CM-phos scaffold, the product yield improved to 94%. In particular, alkenyl tosylates and dialkylsulfoximines were also found to be effective coupling partners under this catalyst system.
Scheme 14 Pd-Catalyzed N-arylation of Sulfoximines with Aryl Sulfonates
Recently, a more electron enriched version of
MeO-CM-phos was prepared by attaching one more methoxy group to the phenyl ring on the ligand skeleton (
(MeO)2-
CM-phos, Scheme 15).
31 This catalyst system was applicable in Pd-catalyzed selective amination of aryl tosylates with arylhydrazines. (
(MeO)2-
CM-phos showed a better catalytic efficacy compared to
CM-phos and
MeO-CM-phos which may enhance the oxidative addition by the electron richness.
Scheme 15. Pd-Catalyzed Mono-N-arylation of Arylhydrazines with Aryl Tosylates
Summary
The Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling and Buchwald-Hartwig amination provide simple and efficient synthetic pathways for constructing carbon-carbon and carbon-nitrogen bonds. The utilization of CM-phos as the supporting ligand allowed the Pd-catalyzed Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reaction and Buchwald-Hartwig amination of aryl/alkenyl tosylates and mesylates for the first time, further expanding the substrate scope of the electrophilic coupling partners beyond conventional aryl halides. A wide range of substrates were found applicable in both Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling processes and amination reactions at low catalyst loadings, demonstrating the versatility of the catalyst system. In addition, the Pd/CM-phos catalyst system was also successfully applied for the synthesis of pharmaceutically relevant intermediates and materials, underscoring its practicability and potential for broader application in organic synthesis. Indeed, the highly tunable CM-phos ligand skeleton allows further fine-tuning through electronic and steric properties, which is potentially useful in addressing more challenging coupling processes.
Copyright © 1921-, Organic Syntheses, Inc. All Rights Reserved