Org. Synth. 2009, 86, 36
DOI: 10.15227/orgsyn.086.0036
2-(2,2-DIBROMOETHENYL)-BENZENAMINE
Submitted by Christopher Bryan, Valentina Aurregi, and Mark Lautens
1.
Checked by Andreas Pfaltz and Ivana Fleischer.
1. Procedure
A. 1-(2,2-Dibromoethenyl)-2-nitrobenzene (2). A 500-mL, three-necked round-bottomed flask equipped with a magnetic stirring bar and fitted with a 125-mL pressure-equalizing addition funnel (capped with a rubber septum), a thermometer and a two-tap Schlenk adaptor connected to a bubbler and an argon/vacuum manifold (Note 1) is sequentially charged at room temperature with 2-nitrobenzaldehyde (4.03 g, 26.4 mmol, 1.0 equiv) (Note 2) and tetrabromomethane (13.13 g, 39.5 mmol, 1.5 equiv) (Notes 3 and 4). Dichloromethane (100 mL) is added into the flask using the addition funnel and the system is purged with argon for 5 min (Note 5). The addition funnel is capped with a rubber septum, and the reaction is kept under argon atmosphere. The resulting yellow solution is cooled to 2-3 °C (internal temperature) with an ice-bath. The addition funnel is re-charged with dichloromethane (20 mL), and then triisopropyl phosphite (15.9 mL, 58 mmol, 2.2 equiv) is added via syringe through the septum and the resulting solution is added dropwise to the stirred mixture in the flask over a period of 60 min (Notes 6 and 7). During the addition of triisopropyl phosphite the internal temperature of the flask is maintained between 3 and 5 °C. The mixture is then stirred (internal temperature, 3 °C) until the starting material has been completely consumed as shown by thin layer chromatography (TLC) (Note 8), at which point the mixture is quenched with sodium bicarbonate (saturated aqueous solution, 85 mL) added through the addition funnel with the stopcock open (Note 9). The mixture is transferred into a 500-mL separatory funnel and the organic phase separated. The aqueous phase is extracted further with dichloromethane (2 × 40 mL) and the combined organic phase is washed once with water (80 mL), transferred into a 500-mL, one-necked, round-bottomed flask and concentrated by rotary evaporation (35 °C, 15 mmHg) to give 27.0-28.5 g of a brown oil (Note 10). The flask containing the crude material is equipped with a water-cooled condenser. Concentrated HCl (12 M, 30 mL) and glacial acetic acid (30 mL) are added (Note 11), the condenser is capped with a two-tap Schlenk adaptor connected to a bubbler and an argon/vacuum manifold, and the resulting mixture is heated to reflux in an oil bath (110 °C external temperature) and stirred for 14 h under an argon atmosphere. The reaction is then cooled to room temperature and distilled water (150 mL) is added. The mixture is neutralized by the portion-wise addition of sodium carbonate (45 g, 0.36 mol) (Note 12). Diethyl ether (150 mL) is added, the contents of the flask are stirred vigorously for 5 min and any solids are removed by vacuum filtration (water aspirator, 20 mbar) through a fritted glass funnel (8.0 cm diameter, porosity 3). The residue is washed with diethyl ether (2 × 20 mL), the filtrate is poured into a 500-mL separatory funnel and the phases are separated. The aqueous phase is extracted with diethyl ether (2 × 100 mL). The combined organic phases are washed with distilled water (2 × 100 mL) and brine (75 mL), dried (MgSO4), filtered (gravity filtration through a fluted filter paper) and concentrated under reduced pressure with a rotary evaporator (30 °C, 15 mmHg) to give 8.01-8.06 g (99 %) of a brown oil (Note 13), which solidified under high vacuum (0.04 mmHg) (Notes 13 and 14). A stir bar is inserted into the flask, heptane (15 mL) is added, and the flask is heated with stirring to 50 °C in an oil bath (external temperature). Ethyl acetate (1 mL) is added, and the solution is decanted into a second 50-mL, round-bottomed flask which is pre-warmed to at least 50 °C to remove any insoluble material (Note 15). The flask is placed in the oil bath, which is allowed to cool slowly. When the temperature of the oil bath has reached 40 °C, the flask is scratched to induce crystallization (Note 16). The flask is then allowed to cool to room temperature, left at room temperature for 1 h and then cooled to 4 °C (refrigerator) for a further 14 h. The product is isolated by vacuum filtration through a fritted glass funnel (3 cm diameter, porosity 4). The crystals are washed with ice-cold heptane (2 × 5 mL) and then dried under vacuum (0.03 mmHg, 14 h) to afford pure 1-(2,2-dibromoethenyl)-2-nitrobenzene (5.95-6.11 g, 73-75 %) as a brown crystalline solid (Note 17).
B. 2-(2,2-Dibromo-vinyl)-phenylamine (3). A 250-mL Büchi autoclave glass vessel (Note 18) is charged with 1-(2,2-dibromovinyl)-2-nitrobenzene (5.80 g, 18.9 mmol) and methanol (100 mL) (Note 19). The solution is stirred until all of the solid is dissolved, at which point vanadium-doped platinum on activated carbon is added (580 mg, 0.015 mmol, 8.0 × 10-4 equiv) (Note 20). The vessel is attached to the autoclave and pressurized to 2.5 bar with hydrogen. The flask is thrice evacuated (via diaphragm pump) and back-filled with hydrogen to 2.5 bar, then stirred for 3 h at room temperature (Note 21). The hydrogen is removed by evacuation, and the suspension is filtered through a pad of celite (2.5 cm in height) (Note 22). The pad is washed with methanol (3 × 80 mL), and the filtrate is concentrated on a rotary evaporator (30 °C, 15 mmHg) and dried under vacuum (0.03 mmHg, 16 h) to afford 5.22 g (99.8 %) (Note 23) of the title compound as an orange oil (Notes 24 and 25).
2. Notes
1.
All glassware was oven-dried, quickly assembled and cooled under vacuum (0.03 mmHg) prior to use. The submitters performed the reaction under an atmosphere of nitrogen.
2.
2-Nitrobenzaldehyde was purchased from Aldrich (>99 %) and used as received.
3.
Tetrabromomethane (98%) was purchased from VWR. It was dissolved in
dichloromethane (30 g in 150 mL), dried over
MgSO4 (10 g), filtered, concentrated by rotary evaporation (30 °C, 15 mmHg), and dried under vacuum (30 °C, 15 mmHg, 4 h) prior to use.
4.
Use of less than 1.5 equivalents of CBr
4 led to a reduced yield, and the formation of small amounts of unidentified by-products. For example, the use of 1.1 or 1.3 equivalents gave a 67-71 % yield after recrystallization.
5.
Submitters used dichloromethane purchased from Caledon (≥99.5 %) and checkers used dichloromethane from J. T. Baker (>99.5%). Checkers and submitters used the solvent as received.
6.
Triisopropyl phosphite was purchased from Alfa Aesar (90 %) and used as received. The reagent may be purified by vacuum distillation over sodium (bp = 65 °C, 15 mmHg); no improvement was observed with purified material.
7.
After the addition of the solution of triisopropyl phosphite, the color of the reaction mixture changes from yellow to dark brown.
8.
Reaction time was 0.5 h. The progress of the reaction was followed by TLC analysis on silica gel plates cut from 20 × 20 aluminum sheets (Submitters used Silica gel 60 F
254 from EMD Chemicals, checkers Polygram® SIL G/UV254 from Macherey-Nagel) eluting with pentane-diethyl ether 9:1. R
f values of the starting material and product are 0.25 and 0.52, respectively.
9.
The temperature rises to 40 °C over the course of the addition.
10.
A small amount of white crystalline material was sometimes observed in the crude product; the presence or absence of this material had no effect on the course or outcome of the purification.
11.
Hydrochloric acid and glacial acetic acid were purchased from Fisher (submitters) or VWR (checkers) and used as received.
12.
Sodium carbonate was added in 20-30 portions, with care taken to ensure that the evolution of CO
2 does not become too vigorous. The temperature rises to 38-40 °C during the addition.
13.
For acid-sensitive substrates, the material may also be purified by chromatography: the crude material is loaded via Pasteur pipette onto a pre-packed silica gel column (7 × 9 cm, ~200 g silica; silica gel 0.040-0.063 mm, pore diameter 6 nm purchased from Silicycle; column made by using a slurry of silica gel and pentane) and eluted with 9:1 pentane/diethyl ether. The product is collected in a single fraction containing the first 1300 mL of eluent, and isolated as a yellow solid after evaporation (30 °C, 20 torr).
14.
According to submitters, this material is sufficiently pure to be used in most reactions (>95% HPLC). However, for catalytic applications, recrystallization may be necessary.
15.
Warming the second flask is essential to preclude premature crystallization. If no insoluble material is observed, this step is omitted.
16.
Addition of a seed crystal is a preferred alternative to scratching; usually, a few crystals are formed during the decanting process.
17.
1-(2,2,-Dibromoethenyl)-2-nitrobenzene has the following physical properties: mp = 60-61 °C,
1H NMR
pdf (500 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 7.54 (t,
J = 7.6 Hz, 1 H), 7.59 (d,
J = 7.8 Hz, 1 H), 7.68 (t,
J = 7.6 Hz, 1 H), 7.78 (s, 1 H), 8.12 (d,
J = 8.2 Hz, 1 H).
13C NMR
pdf (126 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 93.3, 125.0, 129.6, 131.5, 131.8, 133.7, 134.2, 146.9. IR (ATR) 3035, 1609, 1575, 1516, 1338, 1307, 1200, 965, 896, 863, 852, 831, 788, 732, 666 cm
-1. Anal. Calcd. for C
8H
5Br
2NO
2: C, 31.30; H, 1.64; N, 4.56. Found: C, 31.32; H, 1.59; N, 4.48.
18.
The checkers used a pressure autoclave from Büchi Glas Uster (2.5 bar). The submitters used a Parr hydrogenation apparatus (36 psig = 2.48 bar).
19.
The submitters purchased
methanol from ACP chemicals (99%), and the checkers from J. T. Baker (99.8%); both used the solvent as received.
20.
Checkers used 1 % Pt + 0.2 % V on activated carbon (50% wetted powder) available from Strem as catalyst. Submitters used 3% Pt + 0.6% V on activated carbon (66 % water, 290 mg, 0.015 mmol, 8.0 × 10
-4 equiv), donated by Degussa. The catalysts were used as received.
21.
The reaction can be followed by TLC. The R
f value of the product is 0.27 (9:1 pentane-diethyl ether).
22.
The pad is prepared by slurrying Celite with methanol in a fritted funnel (8.0 cm diameter, porosity 3) and filtering the excess methanol.
23.
The reaction was carried out also on the half scale in the same equipment yielding the product as a brown oil (2.59 g, 99%).
24.
The submitters isolated the product as a dark brown solid with mp = 40-42 °C. The checkers isolated the product as an orange oil (at room temperature), which solidified in the refrigerator (4 °C).
25.
2-(2,2-Dibromoethenyl)-benzenamine has the following physical properties:
1H NMR
pdf (500 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 3.66 (bs, 2 H), 6.71 (d,
J = 7.7 Hz, 1 H), 6.81 (t,
J = 7.6 Hz, 1 H), 7.18 (t,
J = 7.6 Hz, 1 H), 7.32 (d,
J = 7.6 Hz, 1 H), 7.34 (s, 1 H).
13C NMR
pdf (126 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 92.9, 115.9, 118.5, 121.8, 129.3, 129.8, 134.1, 143.7. IR (ATR): 3465, 3377, 3059, 3024, 2993, 1615, 1574, 1486, 1453, 1308, 1157, 939, 878, 833, 745 cm
-1. Anal. Calcd. for C
8H
7Br
2N: C, 34.69; H, 2.55; N, 5.06. Found: C, 34.68; H, 2.59; N, 5.04.
Handling and Disposal of Hazardous Chemicals
The procedures in this article are intended for use only by persons with prior training in experimental organic chemistry. All hazardous materials should be handled using the standard procedures for work with chemicals described in references such as "Prudent Practices in the Laboratory" (The National Academies Press, Washington, D.C., 2011 www.nap.edu). All chemical waste should be disposed of in accordance with local regulations. For general guidelines for the management of chemical waste, see Chapter 8 of Prudent Practices.
These procedures must be conducted at one's own risk. Organic Syntheses, Inc., its Editors, and its Board of Directors do not warrant or guarantee the safety of individuals using these procedures and hereby disclaim any liability for any injuries or damages claimed to have resulted from or related in any way to the procedures herein.
3. Discussion
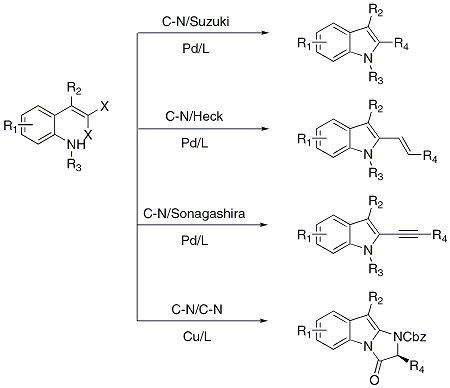
This procedure can be used to prepare a wide variety of
gem-dibromovinyl aniline substrates, which have been used in the synthesis of a number of indoles and indole derivatives by tandem cross-coupling reactions (Scheme 1).
2 This indole synthesis offers the advantages of low cost, mild conditions, and tolerance to a wide range of functionalities.
Scheme 1. Utility of gem-dibromovinylanilines
The Ramirez olefination used in the Corey-Fuchs procedure
3 has traditionally used triphenylphosphine, as well as an aldehyde and CBr
4. Modified methods have been developed to cope with the formation of PPh
3Br
2 as a by-product, with both zinc powder and Et
3N being used as scavenging reagents.
3b,4 The utility of the reaction towards less-reactive ketones, however, remains limited. Alternative non-ylide methods have been developed, including the use of organolithium or Grignard reagents
5 as well as copper-catalyzed redox chemistry between hydrazones and CBr
4.
6 These methods require multiple steps. The formation of triphenylphosphine oxide as a byproduct is also a limitation of this method, especially in large-scale preparations. Significant amounts of triphenylphosphine oxide leads to a tedious purification process, and the highly crystalline nature of triphenylphosphine oxide precludes product purification by recrystallization, requiring column chromatography, which is impractical on large scale.
We have recently reported the use of triisopropyl phosphite as an alternative reagent to triphenylphosphine in the Ramirez olefination.
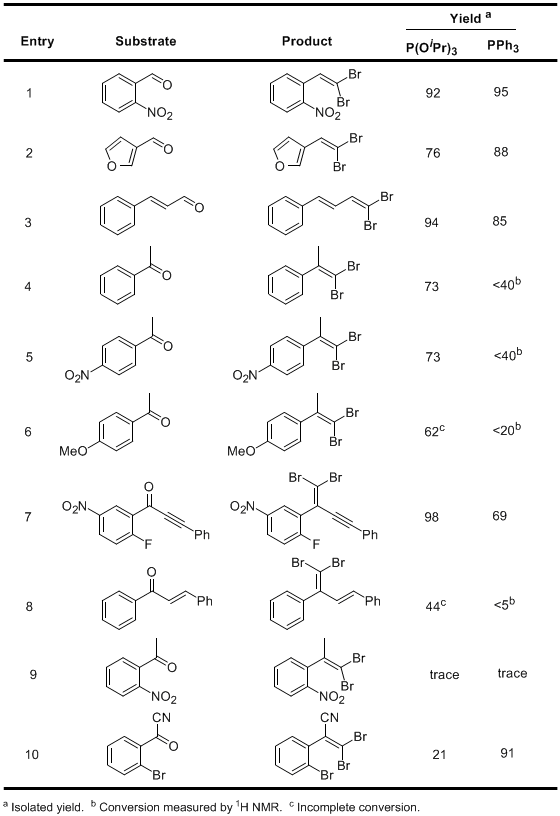
7 It was found that the reaction displays comparable efficiency with both reagents when aldehydes are used as substrates, and the use of triisopropyl phosphite generally gave superior results with ketones (see Table 1).
Table 1. Scope of the P(OiPr)3-mediated Ramirez olefination7
The selective reduction of aromatic nitro groups in the presence of halides and olefins has been accomplished by using either SnCl
2·2H
2O or iron powder in the presence of a catalytic amount of FeCl
3·6H
2O.
2a Both of these methods, however, suffer from the twin drawbacks of large amounts of metal oxide waste (3-7 equiv) and difficulties with workup on large scale. Hydrogenation using traditional catalysts such as Pd/C (1-10%), Ru/C, Rh/C, Pearlman's catalyst (20%) and Raney nickel failed to furnish the desired product for
gem-dibromovinylnitrobenzenes. The use of vanadium additives to promote the hydrogenation of aromatic nitro groups was first described by Baumeister.
8 The vanadium reduces the accumulation of hydroxylamines, which are intermediates in the reduction of nitro groups to amines. Little additional information has appeared in the literature regarding this strategy since the initial report, but our experience suggests that this is the method of choice for the selective reduction of aromatic nitro groups. Yields are comparable or superior to those obtained by redox chemistry with metals (see Table 2), and analytically pure products are obtained simply by removing the catalyst and solvent.
Table 2. Reduction of gem-dihalovinylnitrobenzenes2a
Appendix
Chemical Abstracts Nomenclature (Collective Index Number);
(Registry Number)
2-Nitrobenzaldehyde; (552-89-6)
Tetrabromomethane; (558-13-4)
Triisopropyl phosphite; (116-17-6)
Sodium carbonate; (497-19-8)
Benzene, 1-(2,2-dibromoethenyl)-2-nitro-; (253684-24-1)
Benzenamine, 2-(2,2-dibromoethenyl)-; (167558-54-5)
 |
Christopher Bryan was born in Winnipeg, Canada in 1982. He received his B.Sc. degree with distinction in 2005 from the University of Victoria, where he worked in the laboratory of Scott McIndoe. While an undergraduate, he worked as a Co-op student in the medicinal chemistry department at Boehringer-Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals in Laval, PQ. He is currently pursuing his Ph. D. at the University of Toronto under the supervision of Professor Mark Lautens. His research is focused on the synthesis of heterocycles via metal-catalyzed tandem processes.
|
 |
Valentina Aureggi was born 1977 in Como, Italy. She obtained her Diploma in 1999 and MSci degree in 2003 at Insubria University. During this five-year course of study, her final year project was carried out at the University of Neuchâtel, investigating the synthesis of amido silyloxy dienes under the supervision of Professor Reinhard Neier. Following this, she pursued her PhD from 2003 - 2007 under the supervision of Professor Gottfried Sedelmeier in the Department of Process Research and Development of Novartis Pharma in Basel, obtaining her degree from the University of Neuchâtel. She is currently pursuing post-doctoral research in Professor Mark Lautens's group at the University of Toronto.
|
 |
Ivana Fleischer was born in 1978 in Poprad, Slovakia. She received an M.Sc. degree from Commenius University, Bratislava in 2002, where she performed research under the direction of Professor Stefan Toma. In 2006, after a family break, she started her doctoral studies at the University of Basel, Switzerland, under the direction of Professor Andreas Pfaltz. Her graduate research focuses on mass-spectrometric screening of organocatalysts.
|
Copyright © 1921-, Organic Syntheses, Inc. All Rights Reserved